Gone are the days when you had to drive downtown to get your favorite meal, now getting your food is just one click away. Food Delivery industry has undergone a dynamic change. Food was delivered even in the past but with the technological advancement, food can be ordered online and delivered at customers’ doorstep. Increase in the number of platforms available to customer led the rapid change in the food delivery industry around the world. Worldwide, the largest segment is “Restaurant to Consumer Delivery” with an estimated market volume of $78,734 Mn in 2018. It is expected to generate revenue of $12,033 Mn around the world.
The global online on-demand food delivery services market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 31.76 % during the period 2017-2021. One of the major growth drivers is the convenience and accessibility food delivery enterprises offer. The food delivery platforms makes it easier for consumers to have access to a lot of restaurants under one roof, compare menu, prices and check the customer reviews based on his/her experience.
There is a rise in competition in the Food Delivery Industry due to technological advancement, accessibility to internet, the rise in urban population and an increase in spending. Globally, food delivery industry is very saturated and highly competitive with the presence of major players such as – GrubHub, Just Eat, Seamless, UberEat, and Doordash – along with mid and small size players. Americans dominated the global online on-demand food delivery services market and accounted for a share of more than 40%. This is also due to the presence of almost every major player in the food delivery industry in the US.
China, US, UK, India, and France are the top 5 countries generating maximum revenue in Food Delivery Industry. As a matter of fact, China generates 6 times more revenue compared to revenue in the United States. China’s food delivery industry registered the fastest growth of 23% in 2017 as more and more youngsters are ordering food online.
If we were to breakdown the competition by region- China alone has 37 Bn of food delivery industry. The main two companies that are competing in China are- Ele.me and Meituan.com. According to China Electric Commercial Research Centre (CECRC), Ele.me’s market share was expected to increase from 35% to 53.4 % after its acquisition of Waimai. Its biggest competitor Meituan.com is expected to have a market share of 40.7%.

Deliveroo, emerging from London five-years ago, is now pervasive across the Europe’s main cities. The startup is facing competitions from Ubereats, Amazon, Delivery Hero and Just eats.
In Germany the market share largely belongs to Delivery Hero. In addition to Uber and Amazon, Delivery Hero competes in Europe with JustEat from the UK and Takeaway.com from the Netherlands. Takeaway.com and Delivery hero are fighting for the title of the industry leader, especially in Germany. (Handelsblatt).
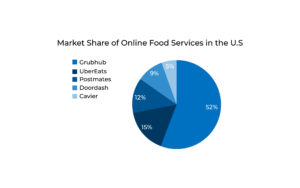
Grubhub is in the leading position in food-delivery industry. After acquiring Eat24 in 2017, its estimated market share in USA is 52%. UberEats, Postmates, Doordash and Cavier have estimated market share of 15%, 12%, 9% and 5% respectively. (Bloomberg)
According to Morgan Stanley, the food-delivery industry of India is valued $19 Bn. Zomato is the leading food delivery company in India (currently valued at 2.5 Bn). It also has presence in 23 countries around the world. The main competitors of Zomato are Swiggy, Foodpanda and Uber eats.
Even though the potential and growth in the market looks promising with the $123 Bn market, margins are still insignificant or non-existent for some major players. However, despite the industry’s current trend, three companies still managed to gain profit. GrubHubs’s net income was reported to be $ 98.98 Mn in 2017. The net income increased by 99.74% from 2016’s. Food delivery startup Delivery Hero announced that its first quarter revenues rose 93% from €63 Mn (£55 Mn) in 2016 to €121 mMn (£105 Mn) in 2017.
Startups like Deliveroo, UberEats, Ele.me and DoorDash haven’t reported any profit yet. Deliveroo says it’s profitable in several undisclosed cities, but annual losses quadrupled, to £129 Mn ($176 Mn), on sales of £129 Mn in 2016. The company’s gross margin is .7-1%. Reasons for low probability is due to companies still being at their embryonic stage. They are investing heavily in developing logistic algorithms to achieve efficiency, incorporating restaurants to their networks and differentiating the business model. Since the market is highly competitive, price war exists and a slight change in price causes consumers to shift to another platform.
To dig deeper into profitability of the companies, let’s look at their cost centers and how revenue is generated. The main cost is incurred for the development of the app ranging from $4,000 to $10,000 per platform depending on the features and complexity of the app. With the app customers, delivery personnel and the restaurant will be able to see real-time how the package is travelling one place to another, time to time, on a real-time basis before it reaches it the delivery point. If the company doesn’t have their own courier system, third party couriers will have to be paid.
The main source of their revenue is generated from commission paid by restaurants ranging from 10%-20% on the total order processed. For example: Restaurants partnering with Seamless can choose from four commission levels (12.5%, 15%, 17.5%, and 20%). The higher the commission the higher the restaurants will appear in the customers’ search engine. On the other hand UberEats and Amazon are said to be charging restaurants a 30% and 27.5% commission. DoorDash usually charges 10% commission. Zomato charges 7% – 8.5% of commissions to its partners. Delivery hero charges restaurants a commission of about 1.60 euros – 10-11 % – on each order, which is lower than many of its competitors. Secondly, revenue is earned from a delivery fee is charged to the customers for each delivery which is approximately $5-$8.
Food delivery industry is still in its early stages of growth. To achieve global growth and economies of scale the food delivery companies need funding and improved logistics to build a strong customer base. It is evident that there is a lot of revenue and value up for grabs here, and those who innovate first will have higher chances of claiming it.




